A precision electronics factory in Shenzhen once encountered a confusing issue: two batches of linear guide rails with the same model (both Class H precision) were installed on the same type of chip testing equipment. However, one batch from a domestic supplier failed after 12 months of use, with obvious rust on the raceway, while the THK guide rails agented by Jingpeng Machinery had no signs of wear after 24 months of operation. The root cause, our engineers found after testing, was the material difference — the failed batch used ordinary carbon steel (S45C), while the THK ones adopted SUJ2 bearing steel with quenching treatment.
Many buyers only focus on precision grades and load parameters when purchasing linear guide rails, but ignore the core factors that determine long-term performance: material and manufacturing process. The service life, wear resistance, and environmental adaptability of guide rails all depend on these two foundations. Today, we will take three typical industry cases to explain how to choose the right material and process for linear guide rails, and how Jingpeng Machinery helps customers avoid "invisible losses" caused by wrong selections.
Material Selection: The "Gene" That Determines Linear Guide Rail Performance
Linear guide rails on the market mainly use three types of materials: carbon steel, bearing steel, and stainless steel. Each has its own applicable scenarios, and blind selection will directly affect the equipment's operation stability. Let's interpret them through actual application cases.
Alibaba Linear Guide Five-Star Store
1. SUJ2 Bearing Steel: The First Choice for High-Precision & Heavy-Load Scenarios
A heavy-duty CNC lathe manufacturer in Changzhou needed guide rails that could withstand a continuous load of 6 tons. Initially, they used SCM440 alloy steel guide rails, but found that the raceway had obvious indentations after 8 months of use, and the machining precision dropped by 20%. Our technical team recommended HIWIN HGH series guide rails made of SUJ2 bearing steel, which was processed by integral quenching and tempering, with a surface hardness of HRC60-62 and a core hardness of HRC30-35 — this combination ensures both wear resistance and impact resistance.
After replacement, the lathe has been operating continuously for 18 months, and the raceway wear is less than 0.005mm, which is far lower than the industry average of 0.01mm. It should be noted that SUJ2 bearing steel is not a "universal material" — its cost is about 30% higher than ordinary carbon steel, so it is more suitable for high-precision machine tools, heavy-duty robots, and other scenarios where performance is prioritized.

2. 304/316 Stainless Steel: The "Protector" in Corrosive & Hygienic Scenarios
A pharmaceutical filling equipment factory in Hangzhou previously used galvanized carbon steel guide rails. Due to the frequent use of ethanol for disinfection in the workshop, the guide rails rusted after 3 months, and the rust chips even polluted the medicinal materials, causing a batch of products to be scrapped. We customized PMI linear guide rails made of 316 stainless steel for them — 316 stainless steel contains molybdenum elements, which have better corrosion resistance than 304, and can withstand the erosion of organic solvents such as ethanol and acetone.
In addition, we also polished the surface of the guide rails to a roughness of Ra0.8, which is easy to clean and meets the GMP certification requirements of the pharmaceutical industry. Up to now, the guide rails have been used for 12 months without rust, and the equipment's qualification rate has increased by 15%. For food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, stainless steel guide rails are not a "cost increase" but a "risk avoidance measure".

3. S45C Carbon Steel: The Cost-Effective Option for General Scenarios
A logistics equipment manufacturer in Guangzhou produces ordinary conveyor lines for carton transportation, with a single guide rail load of only 50kg and no special environmental requirements. They originally planned to purchase SUJ2 bearing steel guide rails, but our team suggested S45C carbon steel guide rails with phosphating treatment — phosphating can form a protective film to prevent rust in general indoor environments, and the cost is 40% lower than SUJ2.
After 2 years of use, the conveyor lines have no problems such as jamming or wear, and the annual procurement cost of the manufacturer is reduced by more than 100,000 yuan. This shows that for general scenarios such as light-load conveying and ordinary assembly lines, S45C carbon steel can fully meet the needs, and blind pursuit of high-grade materials will only cause cost waste.
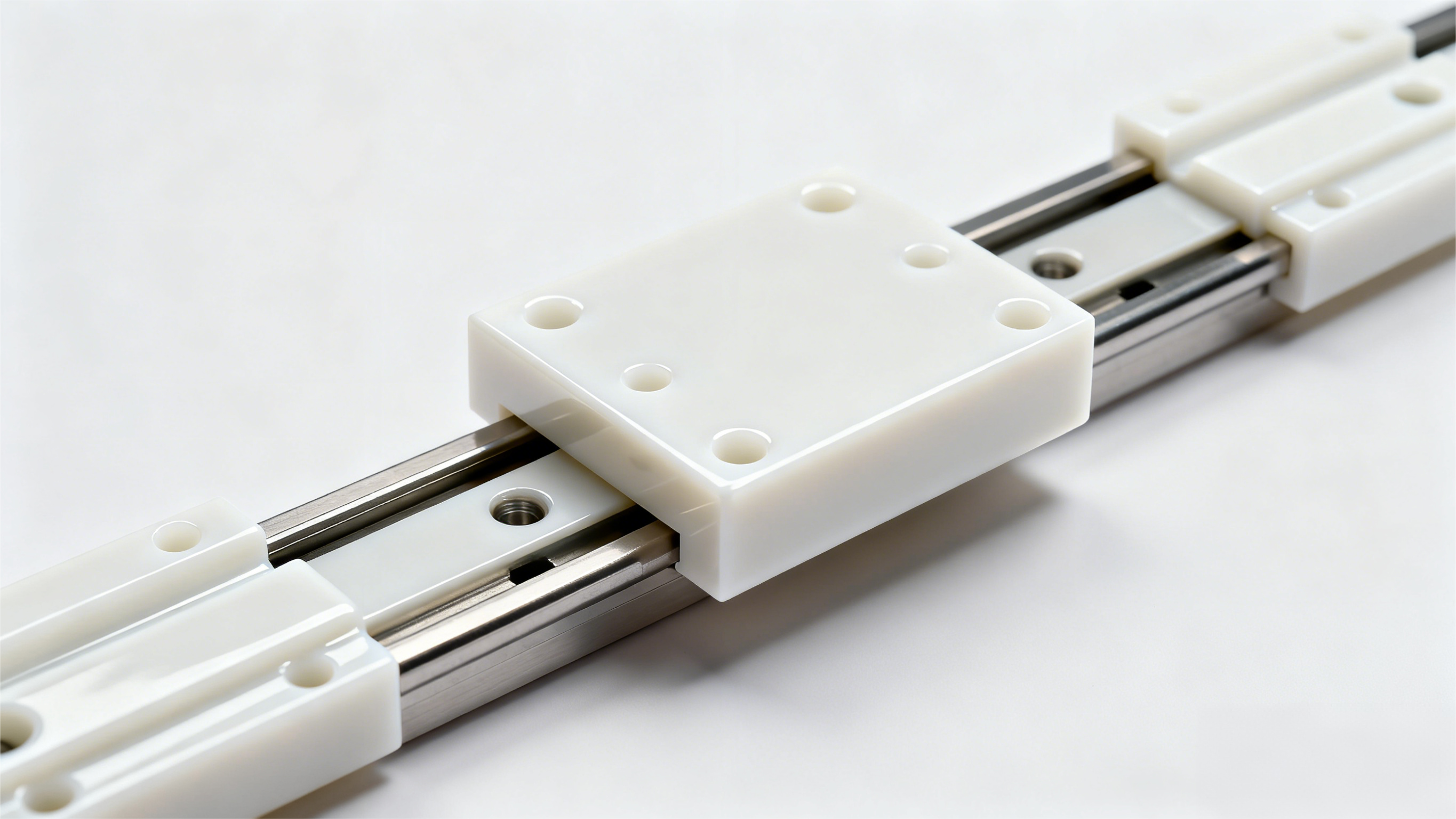
Manufacturing Process: The "Craftsmanship" That Improves Linear Guide Rail Performance
Even with the same material, different manufacturing processes will lead to huge differences in guide rail performance. The two most critical processes for linear guide rails are "grinding vs. rolling" (raceway processing) and "quenching treatment" (hardening process). We will explain their impacts through a comparative case.
-
Grinding vs. Rolling: Precision and Wear Resistance Depend on This A 3C product precision testing equipment factory in Dongguan used rolled linear guide rails before, but found that the repeat positioning accuracy dropped from ±0.005mm to ±0.012mm after 6 months of use. We replaced them with THK ground guide rails — rolled rails use cold rolling forming, with a raceway roughness of Ra0.4-0.8, while ground rails use precision grinding, with a roughness of Ra0.1-0.2, and the straightness error is controlled within 0.02mm/m. After replacement, the equipment's precision remained stable for 15 months. It is recommended that high-speed (speed >3m/s) and high-precision (Class H or above) scenarios use ground guide rails, while general light-load scenarios can choose rolled rails for cost savings.
-
Quenching Treatment: The Key to Extending Service Life Quenching can improve the surface hardness of guide rails. We tested two SUJ2 guide rails: one with surface quenching (hardness HRC58) and one without. In the same heavy-load test (3 tons continuous load), the unquenched one had raceway wear of 0.015mm after 1,000 hours, while the quenched one only had 0.003mm. All guide rails provided by Jingpeng Machinery adopt integral quenching and tempering process, which balances surface hardness and core toughness, avoiding brittle fracture caused by excessive hardness.
-
Surface Coating: The "Additional Protection" for Special Environments For high-temperature (above 150℃) or high-corrosion scenarios, we will add special coatings to the guide rails. For example, a new energy battery sintering equipment factory used guide rails with ceramic coating (Al₂O₃) customized by us, which can withstand high temperatures up to 300℃ and avoid oxidation and deformation of the guide rails in high-temperature environments.
Jingpeng Machinery's Material & Process Matching Scheme: Avoid Waste and Risks
As an authorized agent for THK, HIWIN, and INA, we do not just "sell products" but provide "material and process matching services" based on customer scenarios. Our 3-step matching method has helped more than 3,000 enterprises optimize their selection plans:
-
Scenario Evaluation: On-site investigation of load, speed, temperature, corrosion, and precision requirements. For example, for marine equipment, we will focus on salt spray corrosion resistance and recommend 316 stainless steel with passivation treatment;
-
Material Selection: Match the most suitable material according to the evaluation results, and provide material test reports (such as hardness test, corrosion test) to ensure authenticity;
-
Process Confirmation: Determine whether to use grinding or rolling process, and whether to add surface treatment (such as coating, phosphating) to maximize performance while controlling costs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Material & Process
Q1: How to Distinguish Between Ground and Rolled Guide Rails?
From the appearance: the raceway of ground guide rails is smoother, with no obvious rolling marks; from the data: the precision grade of ground guide rails is generally H3-H5, while rolled rails are C3-C5. We can provide a roughness tester on-site to verify the processing method for customers.
Q2: Is Stainless Steel Guide Rail Definitely Better Than Carbon Steel?
No. Stainless steel has better corrosion resistance but lower hardness (HRC40-45) than quenched carbon steel (HRC58-62), so it is not suitable for heavy-load scenarios. For example, in heavy-duty machine tools, using stainless steel guide rails will lead to premature wear.
Q3: How to Confirm the Material of the Guide Rail Received?
We provide a material certification report (MTC) for each batch of guide rails, which includes elements composition and hardness test results. Customers can also conduct spot checks through third-party testing institutions, and we will bear the testing costs if there is any material inconsistency.
Final Suggestion: Don't Just Look at Parameters, Focus on "Scenario-Material-Process" Matching
The cost of replacing guide rails due to wrong material selection, plus the loss of equipment downtime, is often 5-10 times the procurement cost. Therefore, before purchasing, it is necessary to clarify the core requirements of the scenario, and not blindly pursue high-grade materials or low prices.
If you are unsure about the material and process selection of linear guide rails, feel free to contact Jingpeng Machinery. Our technical team has 10 years of experience in material matching, and can provide free scenario evaluation and selection suggestions. We have service points in Shanghai, Turkey, and Poland, and can respond to your needs quickly.
Table of Contents
- Material Selection: The "Gene" That Determines Linear Guide Rail Performance
- Manufacturing Process: The "Craftsmanship" That Improves Linear Guide Rail Performance
- Jingpeng Machinery's Material & Process Matching Scheme: Avoid Waste and Risks
- Frequently Asked Questions About Material & Process
- Final Suggestion: Don't Just Look at Parameters, Focus on "Scenario-Material-Process" Matching
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 SW
SW
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 BE
BE
 KA
KA
 LA
LA
 MY
MY
 TG
TG
 UZ
UZ


