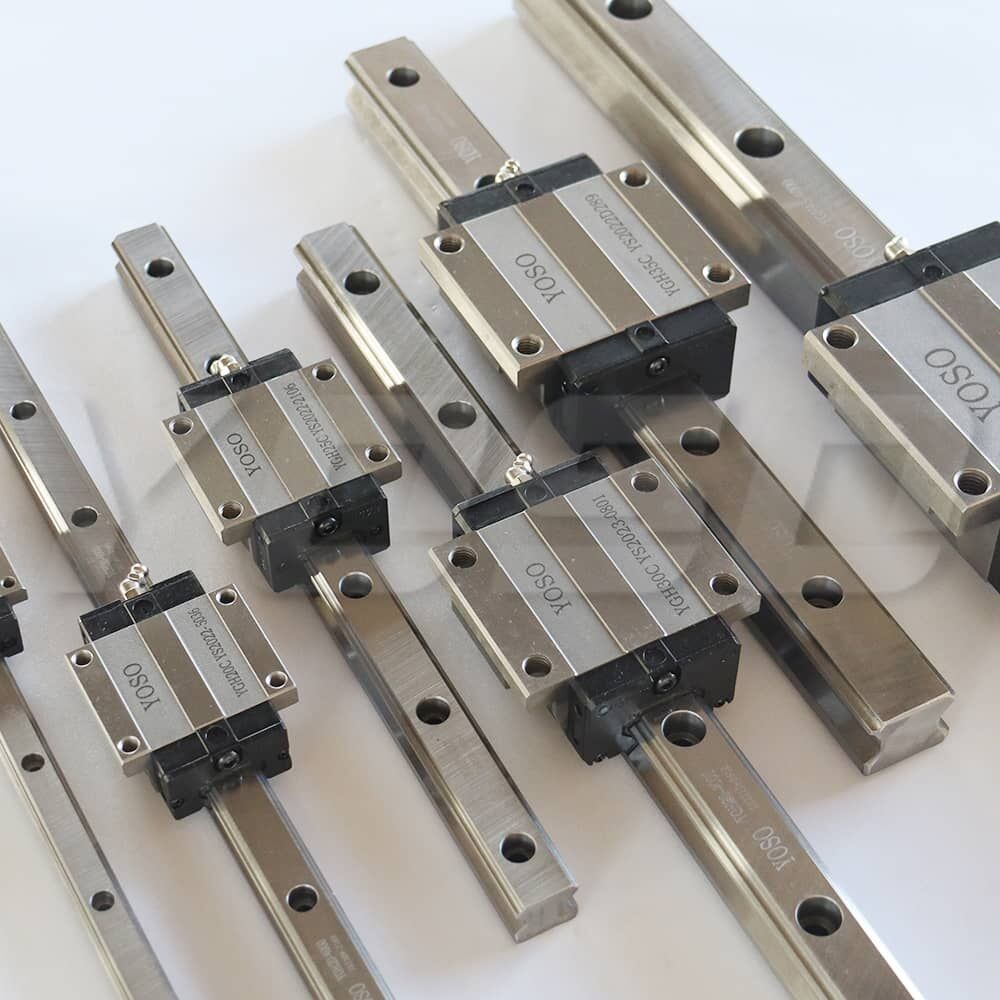
In the field of precision manufacturing and automation, linear guides are core components for achieving high-precision linear motion, and their performance directly determines the operating accuracy, stability, and service life of equipment.
The classification of linear guides is usually based on core dimensions such as load capacity, precision level, structural design, and installation form. On this basis, YOSO MOTION combines industry application scenarios to form a full-scenario product matrix covering light load, medium load, heavy load, and micro-type. Different types of linear guides have significant differences in ball arrangement, guide rail cross-section, and sealing design, thus adapting to different working conditions. The following will analyze the classification and core characteristics of YOSO MOTION's mainstream linear guides one by one.
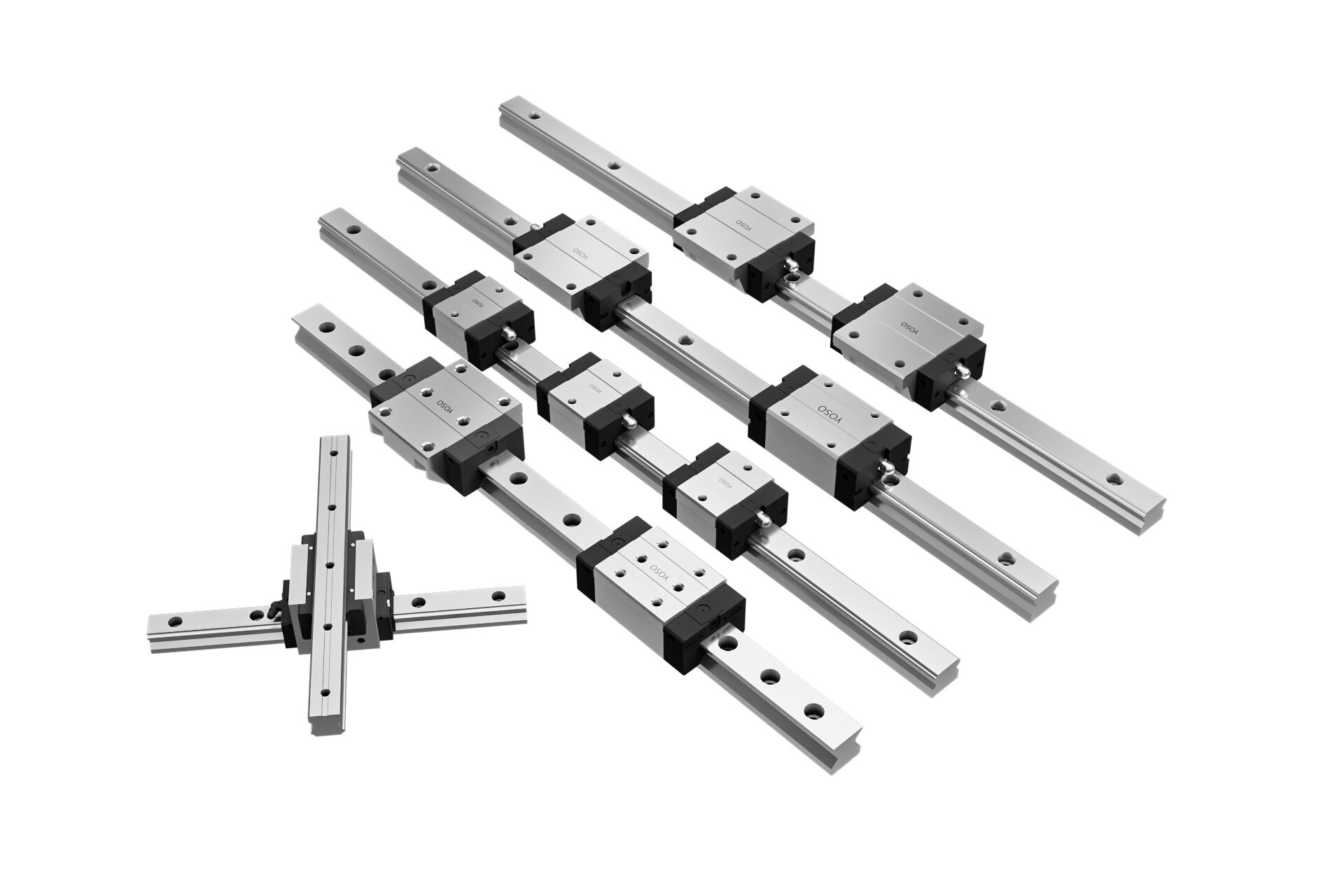

I. Classification by Load Capacity: Full Coverage from Micro-Type to Heavy Load
Load capacity is one of the core bases for the classification of linear guides. YOSO MOTION has designed differentiated products for different load scenarios, forming a complete load adaptation system from micro-type linear guides that can bear several kilograms to heavy-load linear guides that can withstand several tons of load.
1. Micro-Type Linear Guides: YOSO YSS/HIWIN MGN/MGW Series
Micro-type linear guides are products developed for light-load and small-space scenarios. YOSO MOTION MGN (narrow type) and MGW (wide type) series are typical representatives of this category. Their core feature is compact size: the width of the linear guide is usually between 6-15mm, and the shortest slider length is only 16mm, which can easily fit into the compact installation space of precision instruments and small automated equipment.
2. Low-Profile Linear Guides: YOSO YSR/HIWIN EGH/EGW Series
High-load linear guides are the most widely used category in industrial automation. This series of linear guides adopts a four-row arc contact ball arrangement structure, which provides a larger contact area between balls and raceways and more uniform stress distribution. Compared with micro-type linear guides, their load-bearing capacity has achieved a qualitative leap.
The EGH/EGW series has a rated dynamic load range of 8.5-100kN and a rated static load range of 12-140kN, which can adapt to most scenarios such as automated production lines, CNC machine tools, and logistics conveying equipment. Its repeat positioning accuracy is stably maintained at 0.01-0.03mm.
3. High-Profile Linear Guides: YOSO YGH/HIWIN HGH/HGW Series
For heavy-load scenarios such as heavy-duty machine tools, large presses, and port machinery, there is YOSO MOTION YGH/HGH heavy-load linear guide series. The core advantage of this type of linear guide is its super strong load-bearing capacity: its maximum rated dynamic load can reach 280kN, and its rated static load even exceeds 400kN, which can easily cope with working conditions of large loads and strong impacts.
In terms of structure, heavy-load linear guides adopt a multi-row ball circulation design, and some models are even equipped with reinforced slider housings and thickened linear guides to enhance the anti-deformation ability of the overall structure. The raceway adopts a special hardening process, with a surface hardness of up to HRC58-62, which significantly improves wear resistance and service life. In large CNC gantry milling machines, the HGH series linear guides serve as the motion support components of the workbench. While bearing several tons of milling force, they can ensure the motion accuracy of the workbench and avoid the deformation of the linear guides caused by excessive load. In addition, this series is also equipped with a double-sealing structure, which effectively prevents impurities such as dust and iron chips from entering the raceway, making it suitable for harsh heavy-industry environments.
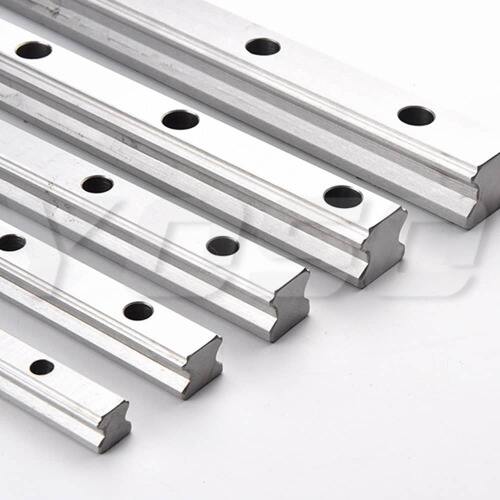
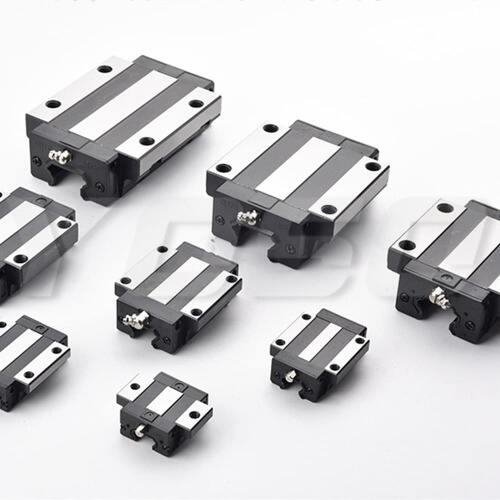


II. Classification by Precision Level: Adapting to Scenarios with Different Precision Requirements
Precision is the core competitiveness of linear guides. According to ISO standards and actual industry needs, YOSO MOTION classifies linear guides into different precision levels, ranging from ordinary precision to ultra-high precision, covering all scenario needs from general machinery to precision instruments. The precision levels of YOSO MOTION linear guides are mainly divided by indicators such as running accuracy (parallelism, perpendicularity), positioning accuracy, and repeat positioning accuracy. Common levels include N (ordinary level), H (high precision level), P (precision level), SP (super precision level), and UP (ultra-high precision level).
III. Classification by Structural Design: Meeting Differentiated Installation and Functional Needs
In addition to load and precision, differences in structural design also lead to different types of linear guides. Based on installation space, motion mode, protection requirements, etc., YOSO MOTION has designed a variety of products with differentiated structures to adapt to complex industrial scenarios.
1. Standard Linear Guides: YOSO YGH/HIWIN HGH/HGW/MGN Series
Standard linear guides are the most widely used category. Their structure is a classic combination of "guide rail + slider", and the slider adopts an integrated design, which is easy to install and suitable for most general scenarios. HGH/HGW and MGN/MGW series all belong to standard linear guides. The advantages of this type of linear guide are strong versatility, easy replacement, and rich accessories. Accessories such as dust covers, grease nozzles, and limit blocks can be matched according to needs to further improve performance.
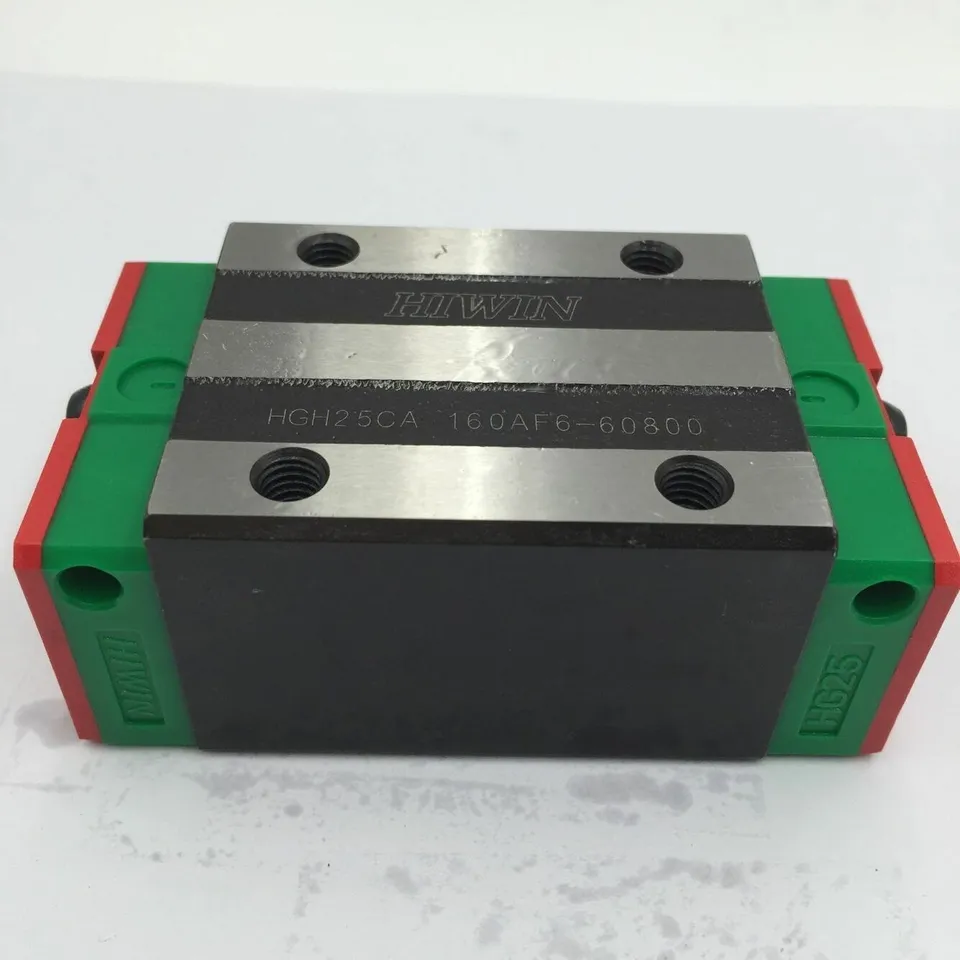

2. Wide-Rail Linear Guides: YOSO /HIWIN WE Series
The core feature of wide-rail linear guides is their larger width, which provides a wider contact area between the slider and the linear guide. They are mainly used in scenarios that require high rigidity and anti-overturning torque. The width of YOSO MOTION WE series wide-rail linear guides can effectively disperse the load and reduce the inclination of the linear guide caused by eccentric load. In large gantry robots and laser cutting equipment, wide-rail linear guides can be used as motion support components for the beam, resisting the inertial force and overturning torque generated during high-speed motion, and ensuring the stable operation of the equipment.
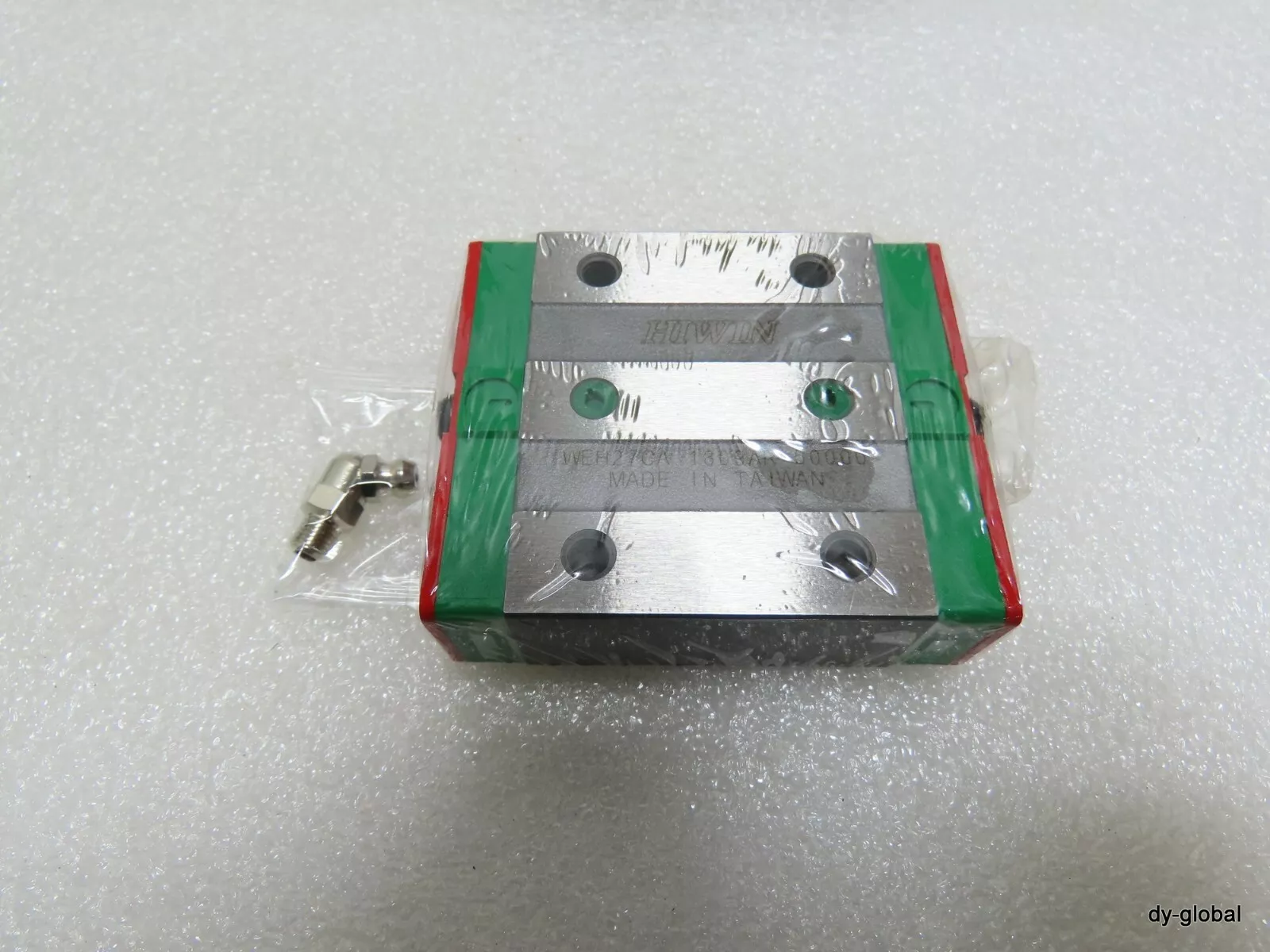

3. Low-Profile Linear Guides: YOSO YSR/HIWIN EGH Series
Low-profile linear guides adopt a compact structural design with a lower slider height, making them suitable for scenarios with limited installation space, such as the internal motion mechanisms of small automated equipment and electronic instruments. The slider height of YOSO MOTION YSR/HIWIN EGH series low-profile linear guides is only about 70% of that of standard linear guides. While ensuring a certain load capacity, they greatly save installation space. Their structural design also integrates the concept of lightweight, using a composite structure of high-strength engineering plastics and metals, which not only reduces weight but also ensures rigidity, adapting to the lightweight needs of precision instruments.
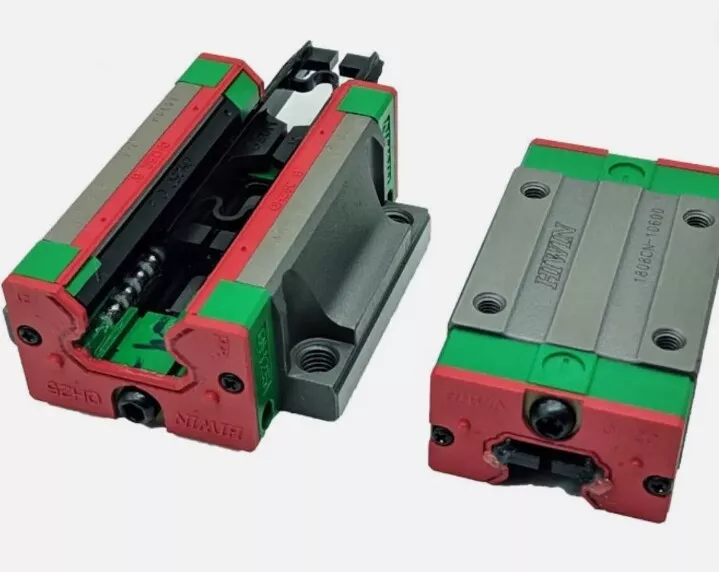

4. Dust-Proof Reinforced Linear Guides: YOSO PGH/HIWIN CGH Series
For harsh environments with dust, chips, and cooling liquid, YOSO MOTION has launched dust-proof reinforced linear guides, such as the PGH-R series. This type of linear guide is equipped with double lip seals and dust scrapers at both ends of the slider, which can effectively block impurities from entering the raceway; some models even adopt a fully enclosed structure. Combined with the long-term sealing of grease, the linear guides can still operate stably in harsh scenarios such as mining machinery and woodworking machinery. In addition, the maintenance cycle of dust-proof reinforced linear guides is extended by more than 50% compared with standard linear guides, which greatly reduces the maintenance cost of equipment.
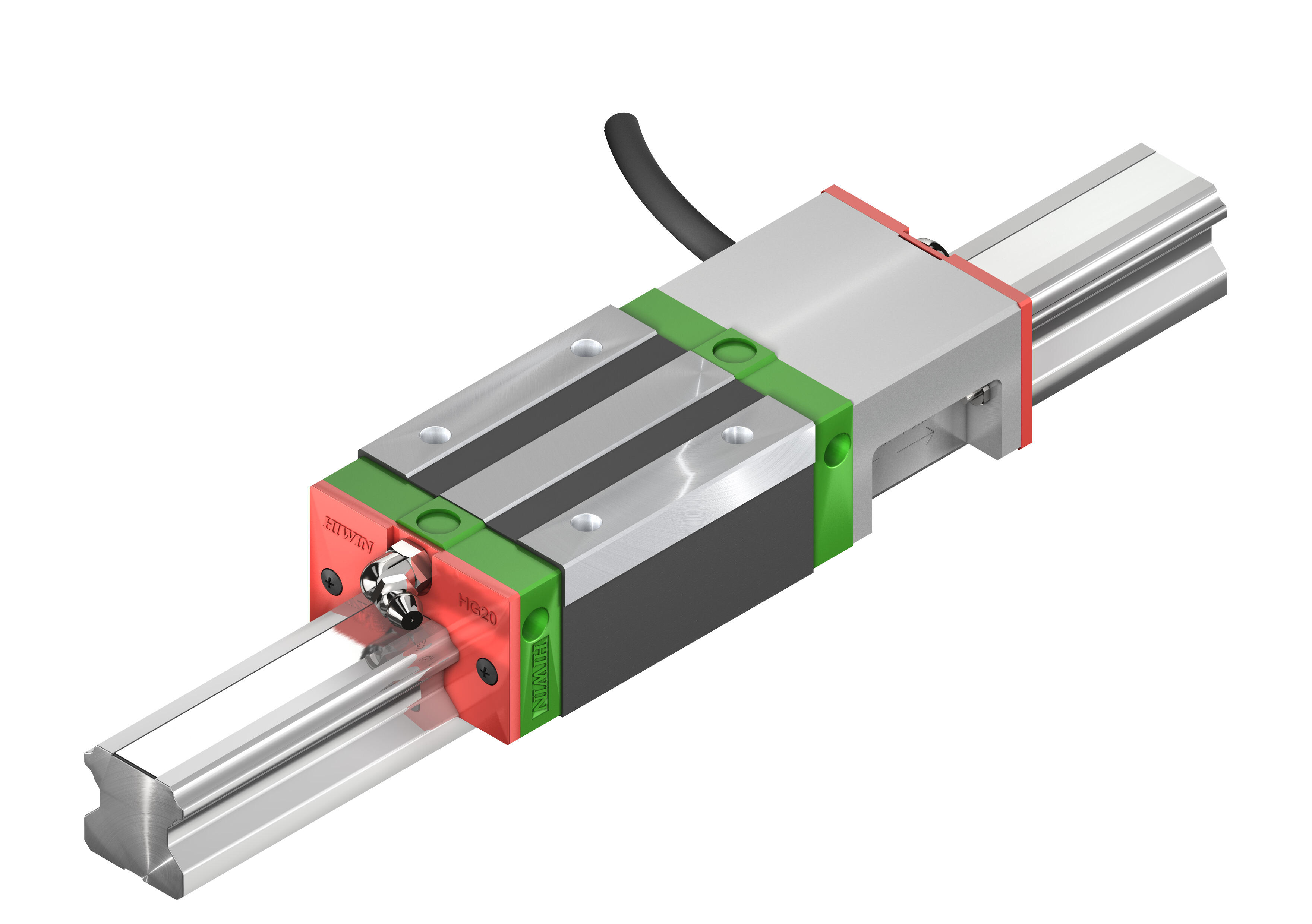
IV. Core Logic for Selecting Linear Guides by Classification (Taking YOSO MOTION as an Example)
After understanding the classification of linear guides, accurate selection needs to combine four core factors: load, precision, space, and environment. The following is the selection logic based on YOSO MOTION series linear guides:
-
Clarify load requirements: For light load (≤12kN), select MGN/MGW micro-type series linear guides; for medium load (12-100kN), select YSR series linear guides; for heavy load (≥100kN), select YGH/YGW series linear guides; for high anti-overturning needs, select WE wide-rail series linear guides.
-
Match precision levels: For general scenarios, select N/H level linear guides; for precision manufacturing, select P/SP level linear guides; for ultra-high precision scenarios (such as semiconductors and optics), select UP level linear guides.
-
Adapt to installation space: For small spaces, select YSR/EGH low-profile series linear guides; for standard spaces, select HGH/HGW standard linear guides; for wide installation, select WE series linear guides.
-
Consider environmental factors: For harsh environments, select PGH/CGH dust-proof reinforced linear guides; for clean environments (such as medical and electronics), select MGN series linear guides and match them with clean grease.
V. Conclusion: The Core Value of Linear Guide Classification Lies in Scenario Adaptation
The classification system of YOSO MOTION linear guides is essentially a precise response to the needs of different industrial scenarios. From micro-precision instruments to heavy industrial equipment, and from clean workshops to harsh working conditions, each type of linear guide has its clear applicable scenarios. For practitioners, mastering the classification logic of linear guides can not only quickly lock in suitable products but also improve equipment performance and reduce overall costs through optimized selection.
The selection logic centered on scenario needs has always been the key to the application of linear guides. For further understanding of the specific parameters or application cases of linear guides, you can refer to YOSO MOTION's official technical manual or contact us directly.
Table of Contents
- I. Classification by Load Capacity: Full Coverage from Micro-Type to Heavy Load
- II. Classification by Precision Level: Adapting to Scenarios with Different Precision Requirements
- III. Classification by Structural Design: Meeting Differentiated Installation and Functional Needs
- IV. Core Logic for Selecting Linear Guides by Classification (Taking YOSO MOTION as an Example)
- V. Conclusion: The Core Value of Linear Guide Classification Lies in Scenario Adaptation
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 SW
SW
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 BE
BE
 KA
KA
 LA
LA
 MY
MY
 TG
TG
 UZ
UZ


